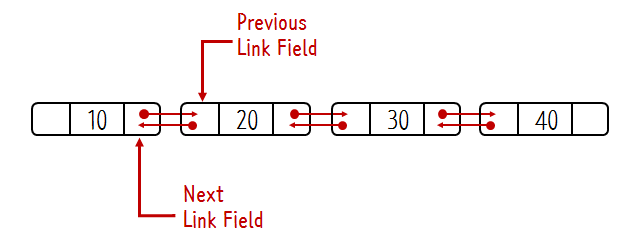
양방향 연결리스트는 노드에 양쪽을 연결해서 previous(이전) next(다음)을 통해 이동할 수 있는 리스트의 형태이다.
이전 노드를 가리키는 변수의 추가로 before를 통해 이전 노드를 기억해야하는 과정을 뺄 수 있다.
 출처:https://opentutorials.org/module/1335/8940
출처:https://opentutorials.org/module/1335/8940
이전에 연결리스트 node에 previous를 가리킬 수 있는 변수만 추가해주면 된다.
-ADT
이전과 동일
단, 노드를 구현하는 부분 이전 노드를 가리키는 pre가 추가됨
typedef struct _node{
Ldata data;
struct _node* next;
struct _node* pre;
}node;
-C 구현 (dummy기반 x)
>헤더파일
#ifndef _DB_LINKED_LIST
#define _DB_LINKED_LIST
typedef int Ldata;
typedef struct _node{
Ldata data;
struct _node* next;
struct _node* pre;
}node;
typedef struct db_linked_list{
node* head;
node* cur;
int size;
}dblist;
typedef dblist List;
void Listinit(List* plist);
void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data);
int Lfirst(List* plist,Ldata* data);
int LNext(List* plist,Ldata* data);
int Lprevious(List* plist,Ldata* data);
int Lsize(List* plist);
#endif
>소스파일
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"DB_LinkedList.h"
void Listinit(List* plist){
plist->head = NULL;
plist->cur =NULL;
plist->size =0;
}
void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data){
//맨 앞에 데이터 추가 양 끝은 null
node* newnode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = plist->head; //처음에는 null, 다음부터는 있음
if(plist->head != NULL){
plist->head->pre = newnode;
}
newnode->pre = NULL;
plist->head = newnode;
(plist->size)++;
}
int Lfirst(List* plist,Ldata* data){
if(plist->head == NULL)
return 0;
plist->cur = plist->head;
*data = plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
int LNext(List* plist,Ldata* data){
if(plist->cur->next == NULL)
return 0;
plist->cur = plist->cur->next;
*data = plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
int Lprevious(List* plist,Ldata* data){
if(plist->cur->pre == NULL) return 0;
plist->cur = plist->cur->pre;
*data = plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
int Lsize(List* plist){
return plist->size;
}
새로운 데이터를 추가하는 과정만 조금 달라졌다.
>> 새로운 노드의 추가 (맨 앞에 데이터 추가)
1. newnode를 할당받고, 데이터 삽입 newnode의 next는 head를 가리킨다.
-1.1 head가 null이 아닐경우 head의 이전 노드를 newnode와 연결한다.
-1.2 head가 null일 경우 -> head에 이전 노드를 연결하지 않는다. head가 null이므로 다음 과정으로 head는 newnode가 되고, 양 끝은 null이 된다.
2. newnode의 pre에 null을 할당한다. 이는 맨 앞에 노드가 추가되는 것이고, 맨 왼쪽의 pre와 맨 오른쪽 next를 null로 만들기 위함이다.
3. head에 newnode를 할당
- dummy기반 C구현 (head와 tail 추가)
헤더파일
#ifndef _DB_liked_dummy
#define _DB_liked_dummy
typedef int Ldata;
typedef struct _node{
Ldata data;
struct _node* next;
struct _node* pre;
}node;
typedef struct db_linked_list_d{
node* head;
node* tail;
node* cur;
int size;
}dblist_d;
typedef dblist_d List;
void Listinit(List* plist);
void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data);
int Lfirst(List* plist,Ldata* data);
int LNext(List* plist,Ldata* data);
int LPrivious(List* plist, Ldata* data);
Ldata LRemove(List* plist);
int Lsize(List* plist);
#endif
소스파일
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"DB_linked.h"
void Listinit(List* plist){
plist->head = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
plist->head->pre = NULL;
plist->head->next = plist->tail;
plist->tail = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
plist->tail->pre=plist->head;
plist->tail->next =NULL;
plist->size =0;
}
void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data){
node* newnode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = plist->tail->pre->next; //초기에는 head->next인 tail
newnode->pre = plist->tail->pre; //초기에는 tail->pre인 head
plist->tail->pre->next = newnode; //초기에는 head->next가 newnode
plist->tail->pre = newnode; //최근 이전노드를 newnode로 두기
(plist->size)++;
}
int Lfirst(List* plist,Ldata* data){
if(plist->head->next == plist->tail) return 0;
plist->cur = plist->head->next;
*data = plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
int LNext(List* plist,Ldata* data){
if(plist->cur->next == plist->tail) return 0;
plist->cur = plist->cur->next;
*data =plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
int LPrivious(List* plist, Ldata* data){
if(plist->cur->pre == plist->head) return 0;
plist->cur = plist->cur->pre;
*data =plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}
Ldata LRemove(List* plist){
node* Rnode = plist->cur;
Ldata Rdata = Rnode->data;
plist->cur->pre->next = plist->cur->next;
plist->cur->next->pre = plist->cur->pre;
plist->cur = plist->cur->pre; //이거 빼먹을뻔!
free(Rnode);
(plist->size) --;
return Rdata;
}
int Lsize(List* plist){
return plist->size;
}
> dummy ListInit
tail과 head를 추가하고 head->next = tail, tail->pre = head로 연결해둔다.
>dummy Insert
1. newnode에 data할당
2. newnode->next = tail->pre->next
>초기에는 tail->pre(next) ->next이므로 tail을 의미
> tail->pre가 newnode로 조정된 후에는 newnode->next의미 but 둘다 tail이긴하다.
3. newnode->pre = tail->pre
>초기에는 head의미
>tail->pre가 newnode로 조정된 후에는 이전 노드를 의미
4. tail->pre->next = newnode
>초기에는 head->next가 newnode가리킴
> tail->pre가 newnode로 조정되면, 이전노드의 next가 새 노드를 가리킴
5. tail->pre = newnode
>dummy remove
삭제할 노드 위치 cur
cur->pre->next = cur->next (이전 노드의 next를 현재 노드의 next와 연결)
cur->next->pre = cur->pre (앞 노드의 pre를 이전 노드와 연결)
cur = cur->pre 현재 노드의 위치도 이전 노드에 옮겨둠
->삭제할 노드의 연결 끊어지고 cur에 위치한 노드는 free로 메모리에서 제거하면 됨
