-
LinkedList(2) - ADT와 구현자료구조와 알고리즘/자료구조 2023. 5. 1. 21:35
1 . ADT
- 단순하게 데이터가 한쪽 방향으로 저장되고, 시작과 끝이 분명한 LinkedList를 구현해 보도록 하자.
- 더미노드 기반으로 head만 존재한다.
- ADT는 배열기반 연결리스트와 크게 차이가 없다. (정렬 추가)
void Listinit(List * plist) > 리스트 초기화
void LInsert(List* plist, Ldata data) >리스트에 데이터를 추가
int LFirst(List* plist, Ldata* data) > 리스트에 저장된 데이터 참조를 위함
int LNext(List* plist, Ldata* data) > 리스트 저장된 데이터 참조
Ldata Lremove(List* plist) >리스트에 저장된 데이터 삭제
int Lcount(List* plist) >리스트 길이 return
void SetSortRule(List * plist, int (*comp)(Ldata d1, Ldata d2)) > 정렬을 위해
*한 쪽방향으로만 데이터를 추가할 것이므로, tail은 필요없고, dummy노드를 두는 이유는 삭제 및 조회의 과정을 일관된 형태로 구성하기 위함이다.
2. 추가,삭제,조회의 과정 살펴보기
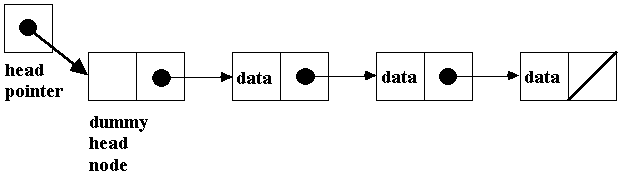
출처:http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~karlaf/CS163_Notes/CS163_Notes%234.htm > 더미노드로 linkedList를 구현하면 다음 그림과 같다.
2.1 추가
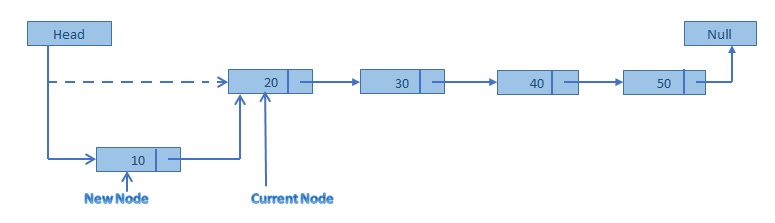
출처: https://scanftree.com/Data_Structure/Insertion-in-linked-list 새 노드를 추가하면, newnode의 next가 기존의 노드를 가리키도록 하고, dummy노드인 head의 next가 new node를 가리키도록 이어주면 된다.
2.2 삭제
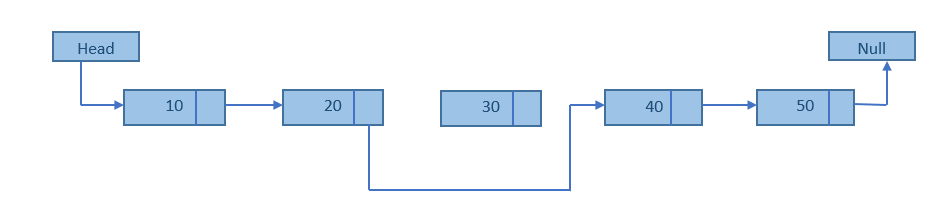
출처: https://scanftree.com 삭제할 노드를 찾고, 그 전의 노드의 next를 후의 노드에 연결한 뒤 노드를 삭제하는 과정을 거친다.
3. 구현
dummy Linked List.h
#ifndef __DUMMY_LINKED_LIST#define __DUMMY_LINKED_LIST
#define false 0#define true 1typedef int Ldata;
typedef struct _node{Ldata data;struct _node* next;}Node;
typedef struct _List{int size;Node* head;Node* cur;Node* before;int(*comp)(Ldata d1, Ldata d2);}LinkedList;
typedef LinkedList List;
void ListInit(List* plist);void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data);
int Lfrist(List* plist, Ldata* data);int LNext(List* plist, Ldata* data);
Ldata LRemove(List* plist);int Lcount(List* plist);
void SetSortRule(List * plist, int(*comp)(Ldata d1,Ldata d2));#endifdummy Linked List .c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include "LinkedListDummy.h"
void ListInit(List* plist){plist->head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); //더미노드 추가plist->head->next = NULL;plist->before= NULL;plist->cur =NULL;plist->size =0;}void LFinsert(List* plist, Ldata data){Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newnode->data = data;newnode->next = plist->head->next;plist->head->next = newnode;(plist->size)++;
}void LSInsert(List* plist,Ldata data){Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(newnode));Node* pred = plist->head; //pred 왼쪽에는 데이터 추가 x 오른쪽에만 가능 따라서 dummy부터 시작newnode->data = data;//새노드가 들어갈 자리를 찾기위한 반복while(pred->next != NULL && plist->comp(data,pred->next->data) != 0){pred=pred->next; //head부터 다음 노드로 이동}newnode->next=pred->next;pred->next = newnode;
(plist->size)++;
//정렬기준은 0 == data<pred->next->data임 (데이터 삽입)// 1== data>pred->next->data인 경우 (이동)}void Linsert(List* plist, Ldata data){if(plist->comp == NULL)LFinsert(plist,data);elseLSInsert(plist,data);}
int Lfrist(List* plist, Ldata* data){if(plist->head->next =NULL){printf("조회할 데이터가 없습니다.\n");return 0;}plist->before = plist->head; //시작점에선 필요없을 것 같지만.. 첫 데이터를 삭제하는 과정에서 필요함plist->cur = plist->head->next;*data = plist->cur->data;
return 1;
}int LNext(List* plist, Ldata* data){if(plist->cur->next == NULL){printf("더 이상 조회할 데이터가 없습니다.\n");return 0;}plist->before = plist->cur;plist->cur= plist->cur->next;
*data = plist->cur->data;return 1;}
Ldata LRemove(List* plist){Node* RemoveNode = plist->cur;Ldata Rdata = RemoveNode->data;
plist->before->next = RemoveNode->next; //삭제는 보통 조회와 같이 이루어짐plist->cur = plist->before; //삭제 후 현 위치는 before과 같음free(RemoveNode);(plist->size)--;return Rdata;
}int Lcount(List* plist){return plist->size;}
void SetSortRule(List * plist, int(*comp)(Ldata d1,Ldata d2)){plist->comp = comp;//정렬기준의 함수는 외부에서 주어짐}dummy Linked List main.c
int compare(int d1,int d2){if(d1<d2) return 0;else return 1;}
int main(void){//사용return 0;}>LSInsert와 SetSortRule함수
외부에서 주어진 정렬기준 함수를 SetSortRule에 전달하고, 이를 comp에 저장해서, 이를 근거로 LSInsert를 작동시킨다.
void LSInsert(List* plist, Ldata data){ Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); Node* pred = plist->head; newnode->data =data; while(pred->next != NULL && plist->comp(data,plist->next->data) != 0) pred =pred->next; } newnode->next = pred->next; pred->next = newnode; (plist->size)++; }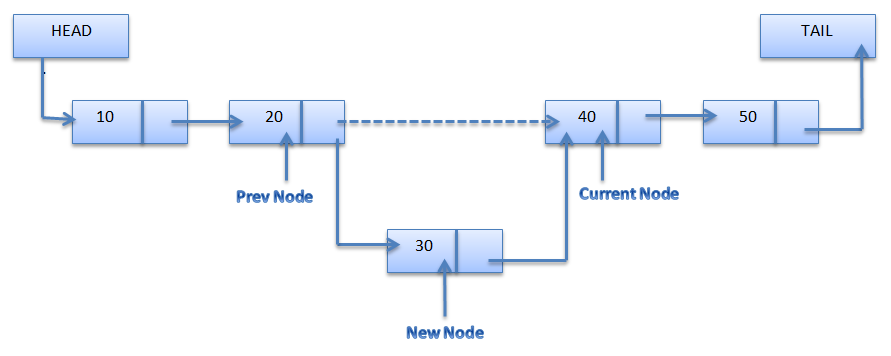
출처:https://scanftree.com > pred는 head부터 시작해서 (pred왼쪽에는 데이터를 추가할 수 없으므로 맨 끝에 위치한 dummy부터 시작)
while문의 조건을 확인하며 옆으로 한칸 한칸 움직인다.
(pred->next == null (끝 의미), plist->comp(data,pred->next->data) == 0 임의로 정한 정렬 기준에 부합)
> 정렬기준이 되는 함수는 main에서 정의해서 list를 초기화한 뒤에 넣어준다.
class LinkedListD<T> { Node<T> head = new Node<>(); Node<T> cur = new Node<>(); Node<T> before = new Node<>(); int size=0; boolean sort; Comparator comp; private class Node<T> { //LinkedListD가 생성되면 이에 맞춰 알아서 결정됨 private T data; private Node next; } void NInsert(T n){ Node<T> newnode = new Node<>(); newnode.data = n; newnode.next = head.next; head.next=newnode; this.size ++; } void SInsert(T n){ Node<T> newnode = new Node<>(); newnode.data = n; Node<T> pred = head; while(pred.next != null && comp.compare(n,pred.next.data) != 0){ pred = pred.next; } newnode.next = pred.next; pred.next = newnode; this.size++; } void Insert(T n){ if(sort == true){ SInsert(n); }else NInsert(n); } boolean LFirst(){ if(head.next == null) { System.out.print("조회할 데이터 없음"); return false; } cur = head.next; before=head; return true; } boolean Lnext(){ if(cur.next == null){ return false; } before = cur; cur = cur.next; return true; } T peek(){ return cur.data; } void setSort(){ this.sort = true; this.comp = new Desending<T>(); } void setSort(Comparator<T> comp){ this.sort = true; this.comp = comp; } int size(){return this.size;} T Lremove(){ T Rdata = cur.data; before.next = cur.next; cur = before; return Rdata; } //기본 정렬 기준 class Desending<T> implements Comparator<T> { @Override public int compare(T o1, T o2) { if (o1 instanceof Number && o2 instanceof Number) { int ob1 = (Integer) o1; int ob2 = (Integer) o2; if (ob1 > ob2) return 0; else return 1; } else if (o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String) { return ((String) o1).compareTo((String) o2) * -1; } return 0; } } }참고자료: 윤성우 열혈자료구조
'자료구조와 알고리즘 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
LinkedList(3) - 양방향 연결리스트 (0) 2023.05.02 LinkedList(3) 원형연결리스트 (1) 2023.05.02 LinkedList (1) (0) 2023.05.01 배열 기반 List (C and java) (0) 2023.03.10 재귀 (0) 2023.03.02